题目
Edit Distance
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
- Insert a character
- Delete a character
- Replace a character
Example 1:
2
3
4
5
6
7
> Output: 3
> Explanation:
> horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
> rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
> rose -> ros (remove 'e')
>
>
Example 2:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
> Output: 5
> Explanation:
> intention -> inention (remove 't')
> inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
> enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
> exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
> exection -> execution (insert 'u')
>
分析
这道题是很经典的字符串编辑距离问题,是动态规划解决问题的一个典型例子。题目问的是我们通过一次只能增加、减少或替换一个字符的操作,最少几次操作能把两个字符串改成相同的字符串。
解法一
使用动态规划来解决问题。
考虑长度为i的字符串str1和长度为j的字符串str2,用dist[i][j]来代表它们之间的编辑距离。
首先,容易知道,如果其中一个字符串为0,那么编辑距离就是另一个字符串的长度,即i = 0时 dist[0][j] = j,j = 0时dist[i][0] = i。
要计算dist[i][j],我们考虑从str1和str2的最后一个字符(char1和char2)入手:
如果
char1 == char2,那么dist[i][j] = dist[i - 1][j - 1],这应该是很容易看出来的,最后一个字符相等,那么有没有它们对编辑距离都没有影响如果
char1 != char2,这时候可以对最后一个字符进行3个操作:- 把
char2替换成char1,那么dist[i][j] = 1 + dist[i - 1][j - 1],这是因为替换后就相当于char1 == char2的情况了,因此只需要加上那替换的开销1 - 在str2最后加一个字符
char1,那么dist[i][j] = 1 + dist[i - 1][j],这相当于给str2加了一个长度,此时的char1 == char2,同样需要额外的开销1 - 删掉str2的最后一个字符
char2,那么dist[i][j] = 1 + dist[i][j - 1],这种情况相当于str2长度减1,当然就是要算dist[i][j - 1]了,同样需要额外开销1
上面对
char2的操作也可以改成对char1的操作,但结果没有区别- 把
根据上面的结论,很容易得到动态规划方程:
1 | dist[i][j] = min(1 + dist[i - 1][j], 1 + dist[i][j - 1], diff(char1, char2) + dist[i - 1][j - 1]) |
根据动态规划可以写出下面的代码,时间复杂度O(mn),空间复杂度O(mn)。
代码
1 |
|
解法二
很多DP算法都可以进行空间复杂度的优化,本题也不例外,通过优化,我们可以把空间花费降至线性。
考虑解法一中的双重循环,转换到如下表格的话,不难知道是一行行地算出结果的。在初始时表格第一行和第一列的值是确定的,这由前面的讨论可以知道。
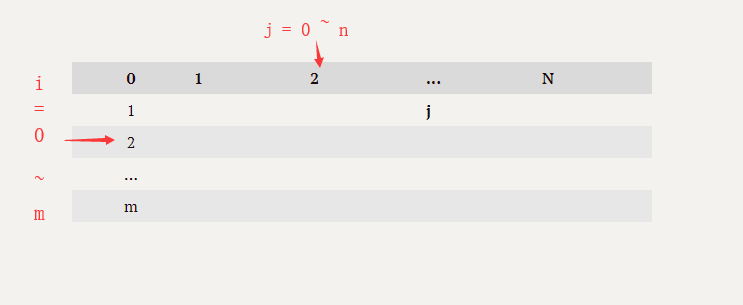
考虑当计算到任意位置的dist[i][j],我们可以由解法一算法得知,dist[i][j]取决于它左边、上面、以及左上角表格的值,现在我们可以考虑把空间压缩到一维了:
dist[n]只存每一行的值,初始情况即第一行。
当要计算dist[j]时,由于我们是从左往右计算每一行的,所以左边的值就是dist[j - 1],而上面的值就是dist[j](因为此时dist[j])还没有被覆盖,存放的仍是上一行的值,而dist[j - 1]就已经被覆盖,存放的是这一行的值。所以我们也能够知道,我们必须事先存储左上角的值,因为会被覆盖,左上角的值即在计算上一个dist[j]时未被覆盖的上面的值。
优化后的代码空间复杂度为O(n),时间复杂度不变。
很多DP算法都可以通过这种画表格的方式来优化空间。
代码
1 |
|